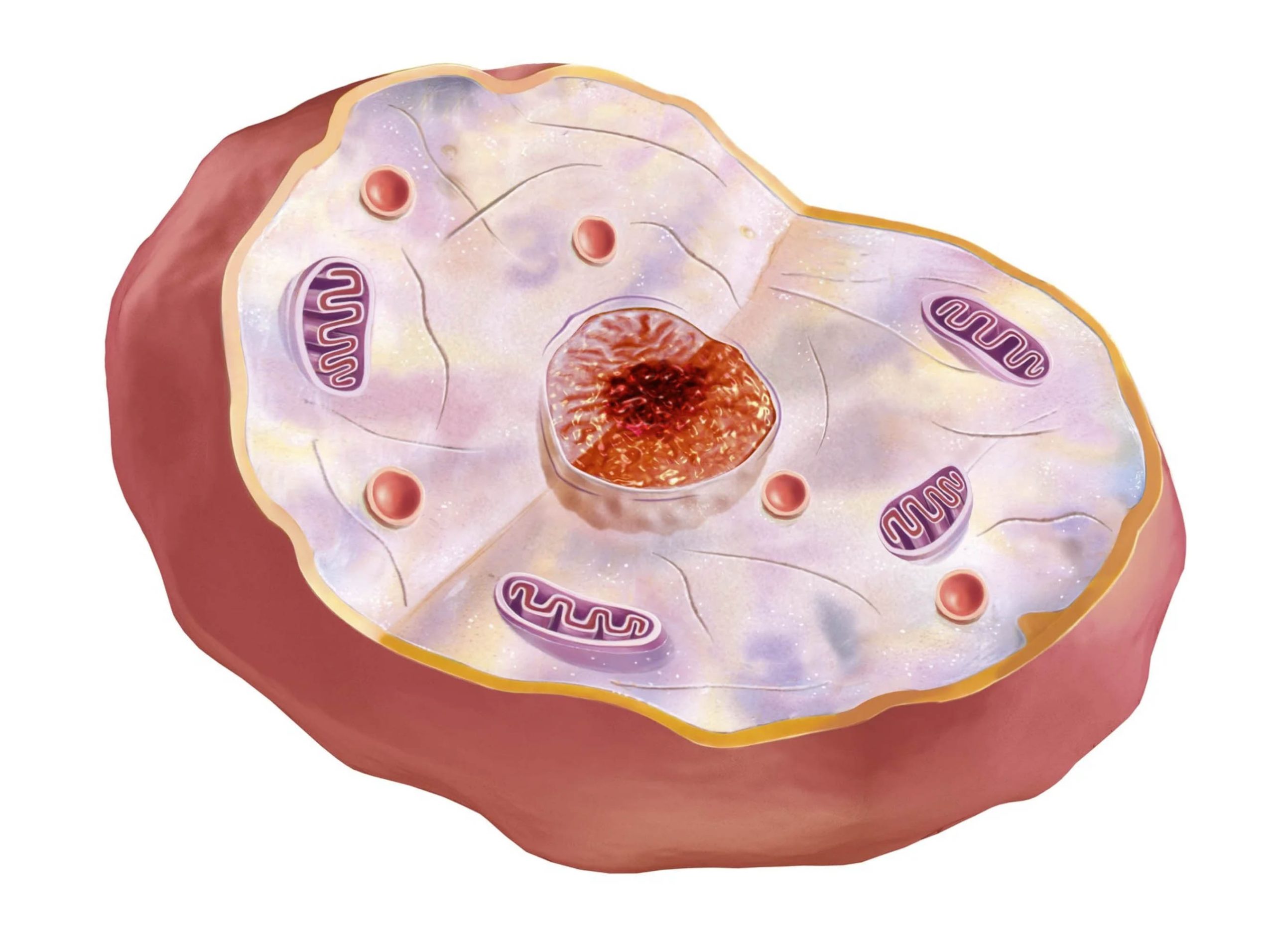
Want to give your cells an extra boost in the fight against free radicals, while promoting overall health and well-being? Increasing your daily Vitamin E intake may help. It’s an easy way to fight free radical damage and reduce damage caused by oxidative stress—a major contributor to premature aging and a precursor for a range of serious health concerns, including diabetes and cancer.
Here’s what you need to know about how your body handles oxidative stress and how Vitamin E can be a powerful antioxidant that improves the strength and resiliency of cells.
Cellular damage from oxidative stress
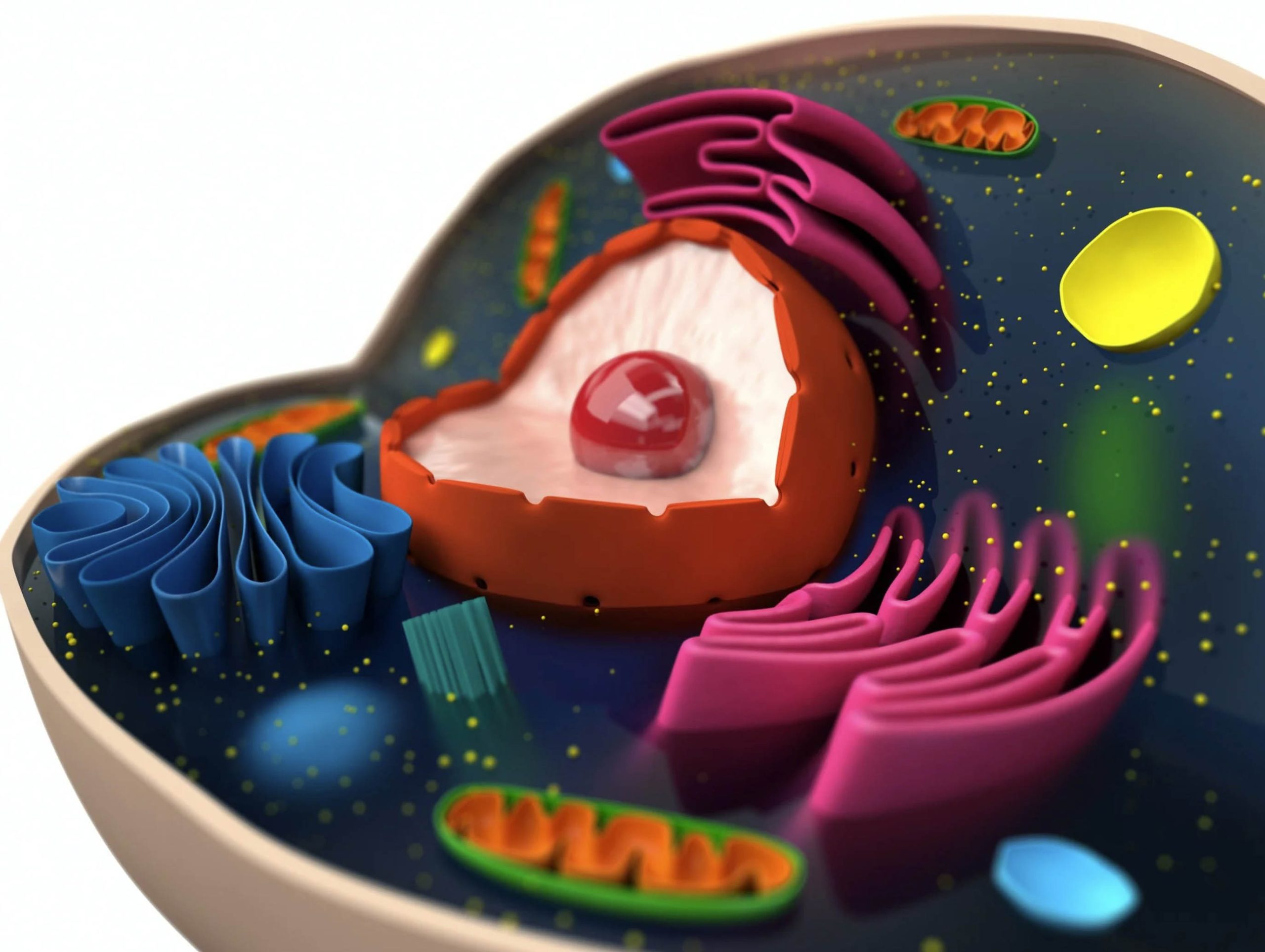
Cells are the building blocks of life, and they’re constantly at risk of damage from free radicals. Free radicals are unstable particles that travel throughout the body looking for an electron to bond with.
While oxidation is an entirely normal process that happens all throughout the course of your life, too much oxidation due to an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants leads to oxidative stress. Many factors contribute to oxidative stress, including diet, exercise habits, and even environmental factors like sun exposure and pollution.
What happens when cells suffer damage?
Free radicals and oxidative stress can damage cells throughout the body. Long-term oxidative stress is generally unhealthy for every body, damaging the body’s cells, proteins and DNA. The free radicals can oxidize important cell components, causing them to lose their ability to function normally. The more damage that accumulates, the more likely it is for cells to die, leading to conditions including chronic inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases and even high blood pressure.
It’s important for adults not just to avoid risk factors for developing long-term oxidative stress, but also to be proactive about fighting it. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle and diet, and, in some cases, taking supplements to fight oxidative stress, like Vitamin E.
How does Vitamin E help?
Vitamin E performs a number of beneficial tasks that work to protect cells in the body from damage. The nutrient protects cell membranes, proteins and DNA from oxidation—it’s your body’s first line of defense from damaging free radicals.
Unlike other Vitamins and nutrients that need constant, daily replenishing, the body actually stores Vitamin E in fat cells. It accumulates in fatty tissue and is released when free radical levels build up in the body and start to cause oxidative stress. Once released, Vitamin E antioxidant cells “donate” an electron to unstable free radicals to stabilize them. As a result, there’s a lower oxidative impact on the body.
Are you getting enough Vitamin E from your diet?
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin E for a healthy adult is around 15mg per day. While there are plenty of foods that contain Vitamin E—including leafy green vegetables, abalone, mangoes, avocadoes and sunflower seeds—most people don’t receive the Vitamin E intake each day that experts recommend.
Some people increase their Vitamin E intake by incorporating Vitamin E-rich oils like sunflower, safflower, hazelnut and almond. Unfortunately, these are oils, and they contain all the unsaturated fats that can be bad for the body. For those with fat-sensitive diets or dietary restrictions that prevent consumption of fatty oils, a Vitamin E supplement like a gel cap, powder or tincture becomes important. Supplements can boost your daily intake of this important nutrient without increasing fat intake.
Natural vs. synthetic Vitamin E
When taking a supplement, an all-natural source of Vitamin E is best to ensure the body gets the most benefits from what you’re taking. All-natural vitamin is readily absorbed by the body compared against synthetic forms. Specific transport proteins in your liver also bind better to natural Vitamin E supplements, giving the nutrient an extra boost as it travels throughout the body.
There’s usually very little difference between all-natural and synthetic supplements, but this is simply not the case for Vitamin E. When it comes to efficient transport and absorption through your body, there’s simply no comparison. The all-natural option is better, and gets this important nutrient exactly where it needs to go in your tissues.
Cells need protection. Vitamin E can provide it.
Vitamin E is an essential nutrient that contributes to your overall health in a variety of ways—most importantly by fighting oxidative damage and extending the life of cells. If your daily Vitamin E intake is on the low side, it’s best to talk with your doctor to determine whether supplementing is ideal for you. With expert guidance, you can choose an all-natural Vitamin E supplement in a concentration that’s best for your body.